What is Decentralized Finance (DeFi)?
Today let’s have a look at the definition of Decentralized Finance, or in short DeFi.

Contents
Part 1: What is Decentralized Finance?
Decentralized Finance (DeFI) includes all the important financial applications you know from more traditional centralized finance, with the key benefit being that there is no centralized institution you’re required to trust.
Part 2: Applications

Decentralized financial applications include: Lending and borrowing, trading, asset tokenization, distribution of dividends, and more.
Part 3: Sender > Receiver
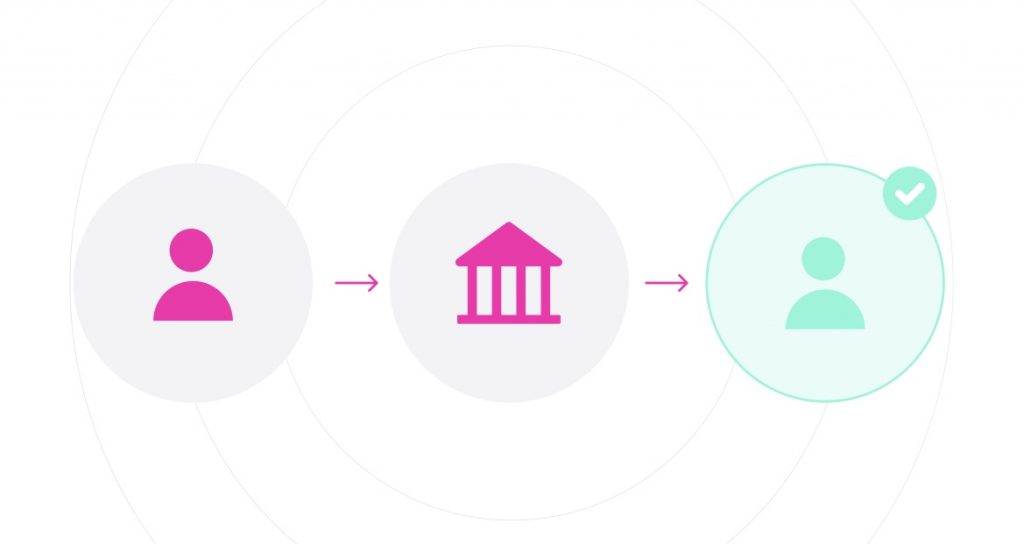
A typical financial transaction looks like this: Sender – Bank – Receiver. Decentralized finance cuts out the middle step, making decentralized financial transactions look like this: Sender > Receiver.
Part 4: Financial Freedom For All
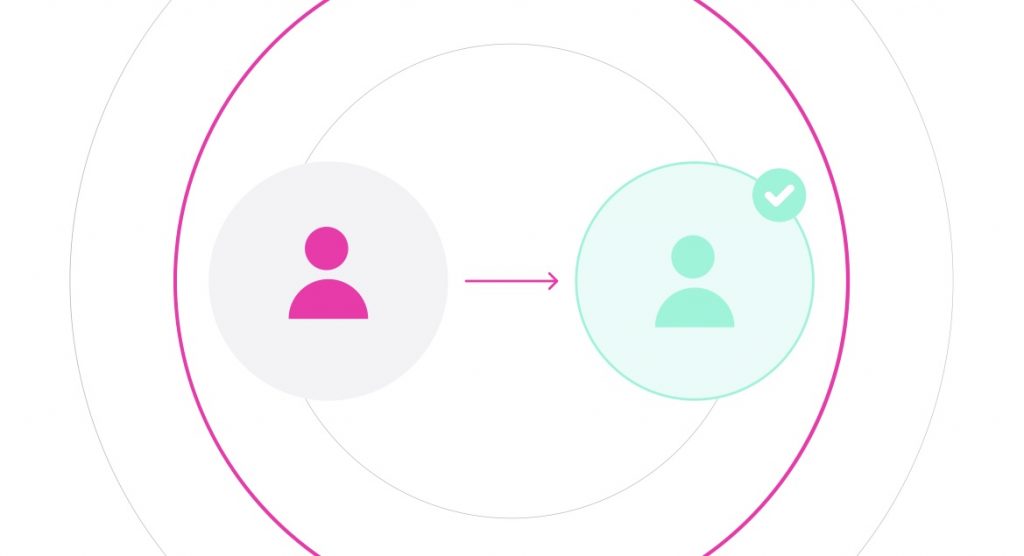
Trustless financial applications without an intermediary (i.e. a bank) enables true financial freedom for all, accessible and usable by anyone all around the world. Borderless, without any gatekeeper.
Part 5: Long-Term Security
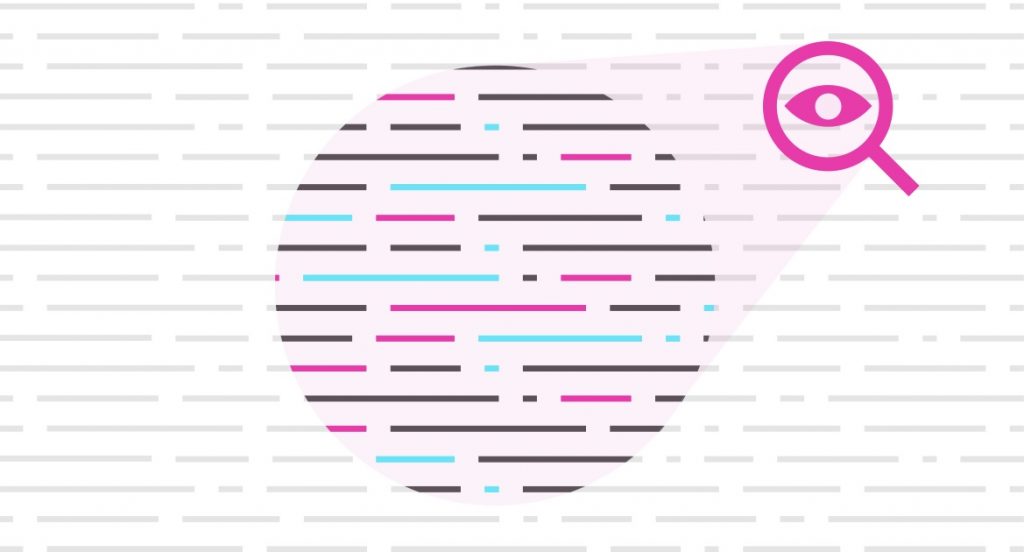

All decentralized finance must be open-source by nature. This level of heightened transparency contributes to long-term security, allowing people to verify the code themselves without the need to trust anyone or anything other than pure mathematics.
Part 6: Decentralized Trading Functionality
DeFiChain already has decentralized trading functionality live and working, with lending and borrowing, as well as asset tokenization coming in Q3 2021. Soon you’ll be able to buy Tesla, Apple and more directly on the blockchain in a decentralized way!

Also Read:
- What is DeFiChain?
- #NativeDeFi vs. DeFi on Ethereum
- DeFiChain: Earn Incredibly High Yields
- DeFiChain: The Decentralized Exchange
Ciao Daniel 🙂
Follow Me on YouTube, Facebook, and Instagram.
If you find this helpful: Share It with your friends!